What is CPVC
Demo Bản Tiếng Anh
Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) is an important engineering thermoplastic due to its:
- Relatively low cost
- High glass transition temperature
- High heat distortion temperature
- Chemical inertness
- Outstanding mechanical, dielectric, and flame and smoke properties
CPVC was first commercialized by Lubrizol in the early 1960s and has since proven its value in a variety of industrial applications where high use temperature and corrosion resistance are desirable.
Today, Lubrizol’s CPVC material is sold under three brand names: Corzan® Material and Piping Solutions (industrial and commercial plumbing applications), BlazeMaster® Fire Protection Systems (fire sprinkler systems) and FlowGuard Gold® Pipe and Fittings (residential and commercial plumbing).
What is CPVC?
Conceptually, CPVC is a PVC homopolymer that has been subjected to a chlorination reaction. Typically, chlorine and PVC react according to a basic free radical mechanism, which can be brought about by various approaches using thermal and/or UV energy.
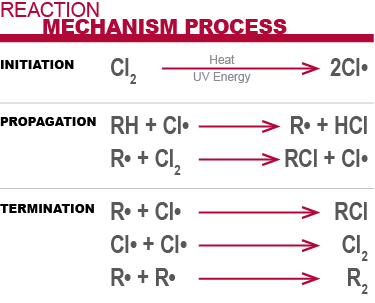
What Is the Difference Between CPVC and PVC?
In PVC, a chlorine atom occupies 25% of the bonding sites on the carbon backbone, and the remaining sites are filled by hydrogen.
CPVC differs from PVC in that approximately 40% of the bonding sites on the backbone are filled with chlorine atoms. The chlorine atoms surrounding the carbon backbone of CPVC are large atoms that protect the chain from attack.
The chlorine content of base PVC can be increased from 56.7% to as high as 74%, though typically most commercial CPVC resins contain 63 to 69% chlorine.
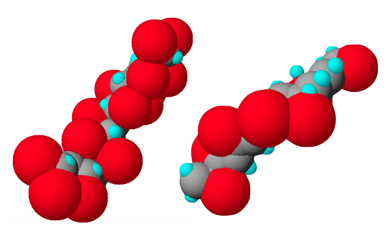
Diagram of CPVC (left) at a molecular level compared to PVC (right). The red spheres represent chlorine elements.
Increased Temperature Resistance
As the chlorine content in CPVC is increased, the glass transition temperature (Tg)—temperature region where the polymer transitions from hard, glassy material to a soft, rubbery material—increases significantly.
It’s the additional chlorine molecules that protect the polymer’s carbon backbone, which in turn protects its structural integrity against heat.
The increased heat resistance allows CPVC to perform at higher operating pressures.
CPVC Additives
CPVC resin is then infused with additives to enhance many of the CPVC resin’s inherent properties, while easing its processability.
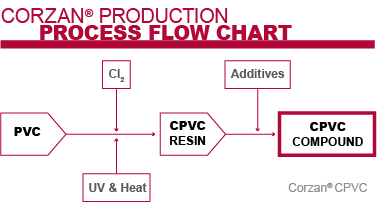
It’s this process that really starts to set CPVC apart from other thermoplastic and metal piping systems, and fortifies it against the demanding environments of industrial plants.
Basic Physical Properties of CPVC
CPVC is inherently inert to acids, bases, and salts, all of which tend to eat away at metals. It’s this inherent chemical resistance, coupled with its temperature and pressure resistance, that enables its use in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
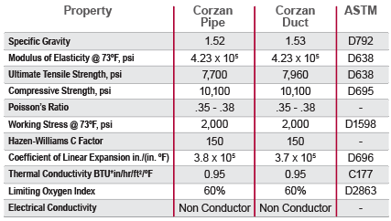
Other key properties of Corzan® CPVC are listed in the table below. You can also see more details in the piping specification and ducting specification sections.
CPVC Product Types
CPVC is a flexible, versatile compound that can be manufactured or fabricated into a number of product forms or geometries using standard molding techniques, primarily extrusion and injection molding.
- Pipe and Fittings: The corrosion and temperature resistance remain, while pressure ratings required of an application can vary with schedule, pipe size, compound type and temperature.
- Ducting: With increasing air emission regulations, the need for reliable fume handling systems, especially in corrosive environments, is growing rapidly. CPVC is available in round duct, fabricated duct fittings, industrial sheet, and welding rod. These components can be designed and fabricated into entire fume handling systems.
- Sheet and Lining: The excellent corrosion resistance and fire performance of CPVC can be applied to various industrial applications and be overwrapped with Fiber Reinforced Polyester (FRP).
- Custom Fabrication and Injection Molded Parts: Corzan CPVC cuts cleanly and is easy to weld, making it ideal for products like tower packing, hoods for specialty exhaust and holding tanks for acids and bases.
Common Applications of CPVC
The basic physical properties of CPVC make it a commonly specified choice in applications ranging from chemical processing plants and mineral processing plants to residential homes and hotel plumbing. CPVC is a problem-free, long-lasting solution for the harshest industrial environments, and is often specified in the following industries:
- Chemical Processing: Reliably transport aggressive chemicals at high temperatures, under pressure, without corrosion concerns.
- Chlor-Alkali: Transport chemicals through some of the most corrosive environments imaginable without corrosion concerns.
- Commercial Plumbing: Eliminate corrosion, reduce maintenance costs and improve overall reliability.
- Mineral Processing: Withstand the demands of precious and raw material processing operations.
- Power Generation: Stand up long term to the high pressures and corrosive chemicals commonly used by power plants.
- Semiconductor: Meet the high purity standards for cleanrooms and eliminate corrosion concerns caused by aggressive chemicals.
- Wastewater Treatment: Put an end to corrosion, even when transporting the most aggressive disinfection chemicals.
CPVC Installation
The recommended joining method for CPVC installation will depend on the product type, but across-the-board, CPVC offers the following installation advantages:
- Lightweight: CPVC is approximately 1/8th the weight of comparably sized steel, which helps to reduce worker strain and injuries, and eliminates the need for heavy equipment.
- Easy to cut: Compound properties make CPVC easier to cut than metals, allowing for more efficient on-site fabrication.
- Simple to install and maintain: CPVC installation requires no complex tools, electricity or highly skilled (and expensive) labor.
- Safer: No open flame or ignition sources are required to join the material.
There are a variety of seam welding options designed to effectively seal components together while maintaining the structural integrity of the material. Recommended installation methods will vary by product type:
- Pipe and Fittings: Solvent cementing, hot-air welding, hot-plate welding, threading, and flanging.
- Ducting: Solvent cementing, hot air welding, thermoforming, extrusion welding and hot-plate welding.
- Sheet and Lining: High speed hot air welding and hot plate butt welding.
Why Not All CPVC Is the Same
While some bottom-line benefits of CPVC are common regardless of manufacturer, CPVC compounds are often differentiated by the level of performance they provide. Not all CPVC systems perform equally.
In the same way that two different types of industrial metallic pipe will likely perform differently, two CPVC industrial pipes made from different compounds will also likely yield different results. That’s why it’s important to choose the very best: Corzan CPVC is backed by rigorous in-house and third-party testing to ensure only the highest quality.
Corzan Material and Piping Solutions and our manufacturers, for example, have undergone different types of tests regarding:
- Minimum burst pressure requirements
- Dimensional tolerances
- Residual stress requirements
- Drop impact requirements
- Fusion property testing
Where to Buy Corzan® CPVC
Only partners with a proven track record of quality and reliability may manufacture products with Corzan CPVC. These manufacturers are carefully chosen to convert Corzan CPVC into the high-performance piping systems, ducting, sheets and lining and more that our customers rely on.


